产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
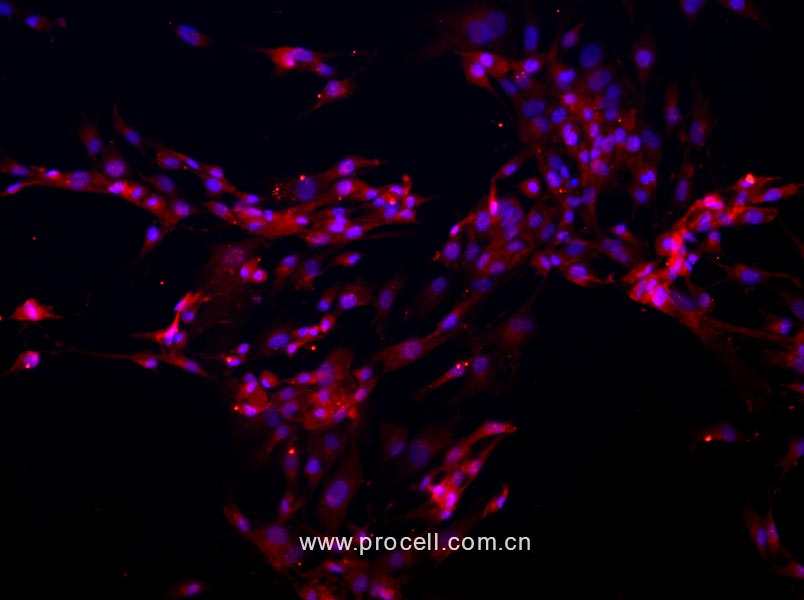
人椎间盘髓核细胞
Human Intervertebral Disc Nucleus Pulposu Cells
货号:CP-H097
规格:5×10⁵Cells/T25培养瓶
价格: ¥询价
培养基货号: CM-H097
产品概述
人椎间盘髓核细胞
Cat NO.: CP-H097
-
产品名称:人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
英文简称:NPCs
-
组织来源:椎间盘组织
-
产品规格:5×10⁵Cells/T25培养瓶
-
细胞简介:
人椎间盘髓核细胞分离椎间盘组织;椎间盘是位于脊柱两椎体之间,分为中央部的髓核,富于弹性的胶状物质;周围部的纤维环,由多层纤维软骨环按同心圆排列。上下有软骨板,是透明软骨复盖于椎体上,下面骺环中间的骨面。上下的软骨板与纤维环一起将髓核密封起来。纤维环由胶原纤维束的纤维软骨构成,位于髓核的四周。纤维环的纤维束相互斜行交叉重叠,使纤维环成为坚实的组织,能承受较大的弯曲和扭转负荷。髓核,是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。髓核在出生时体积大而松散,位于椎间盘的中央,至成年时位置移至椎间盘的中后部;在成年以前构成髓核的主要物质是大量蛋白多糖复合体、胶原纤维和纤维软骨,随着年龄的增长,髓核中的蛋白多糖解聚增多,水分逐渐减少,胶原增粗并逐渐被纤维软骨所替代。
-
方法简介:
普诺赛实验室分离的人椎间盘髓核细胞采用胶原酶-中性蛋白酶混合消化法并结合软骨细胞专用培养基培养筛选制备而来,细胞总量约为5×10⁵cells/瓶。
-
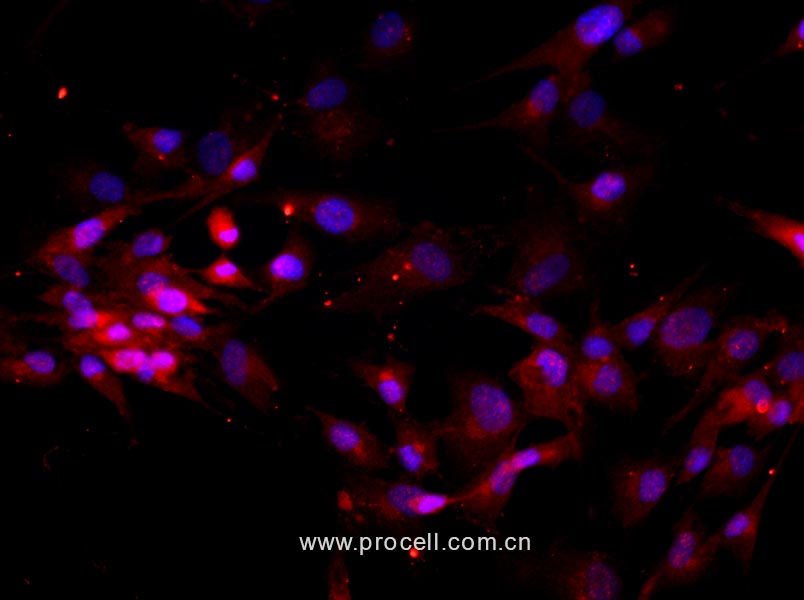
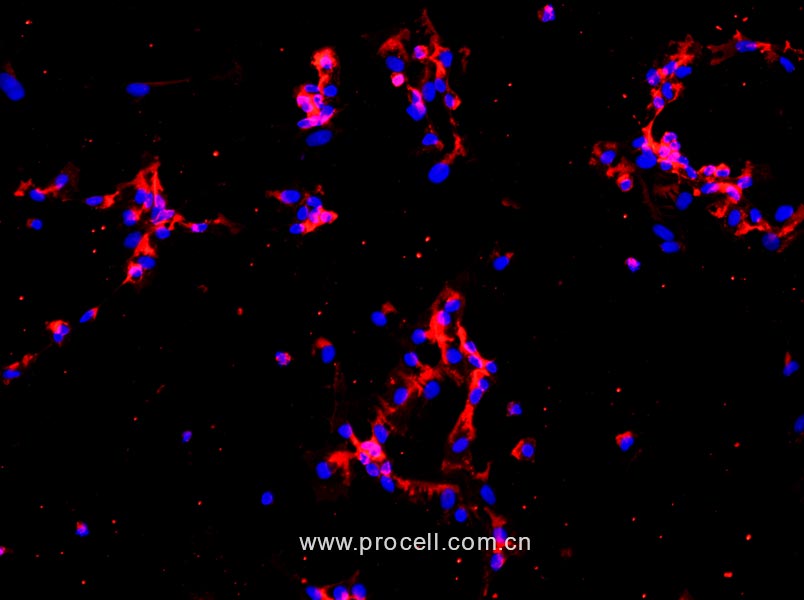
质量检测:
普诺赛实验室分离的人椎间盘髓核细胞经Ⅱ型胶原蛋白免疫荧光鉴定,纯度可达90%以上,且不含有HIV-1、HBV、HCV、支原体、细菌、酵母和真菌等。
-
培养信息:
培养基 含FBS、生长添加剂、Penicillin、Streptomycin等 产品货号 CM-H097 换液频率 每3-4天换液一次 生长特性 贴壁 细胞形态 梭形、多角形 传代特性 可传5代左右;3代以内状态最佳 消化液 0.25%胰蛋白酶 人椎间盘髓核细胞体外培养周期有限;建议使用普诺赛配套的专用生长培养基及正确的操作方法来培养,以此保证该细胞的最佳培养状态。
参考文献
-
Platelet-rich plasma-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway-mediated pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration via the MALAT1/microRNA-217/SIRT1 axis (2024-02-17)
作者:Xueqiang Tao:1.Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang, China; Department of Orthopaedics, The Fourth Hospital of BaoTou, Baotou 014030, Inner Mongolia, China. ; Fen Xue:1.Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Fourth Hospital of BaoTou, Baotou 014030, Inner Mongolia, China. ; Jiayuan Xu:1.Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang, China. ; Wenbo Wang:1.Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang, China. Electronic address: 201803022@hrbmu.edu.cn. ;
期刊:Platelet-rich plasma-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway-mediated pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration via the MALAT1/microRNA-217/SIRT1 axis
DOI:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111106
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞 , 人椎间盘髓核细胞完全培养基
-
Trigonochinene E promotes lysosomal biogenesis and enhances autophagy via TFEB/TFE3 in human degenerative NP cells against oxidative stress (2023-02-18)
作者:Zhenpeng Niu:1.School of Basic Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, Guizhou 550025, China; State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650201, China; Research Unit of Chemical Biology of Natural Anti-Virus Products, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China. ; Guihua Tang:1.State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650201, China. ; Xuenan Wang:1.State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, Yunnan 650201, China; Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan 650032, China. ; Xu Yang:1.State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany Chinese Academy of
期刊:Trigonochinene E promotes lysosomal biogenesis and enhances autophagy via TFEB/TFE3 in human degenerative NP cells against oxidative stress
DOI:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154720
影响因子 :7.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Pharmacological network analysis of the functions and mechanism of kaempferol from Du Zhong in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) (2023-03-03)
作者:Xiaobin Wang:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Yanlin Tan:1.PET/CT Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Fusheng Liu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Jingyu Wang:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Fubin Liu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Qianshi Zhang:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410011, China. ; Jing Li:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Spinal Deformity Center, The Second Xian
期刊:Pharmacological network analysis of the functions and mechanism of kaempferol from Du Zhong in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD)
影响因子 :6.6
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
hASCs-derived exosomal miR-155-5p targeting TGFβR2 promotes autophagy and reduces pyroptosis to alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration (2023-03-14)
作者:Dong Chen:1.Department of Orthopaedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No.2 Yinghua East Street, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China. ; Xin Jiang:1.Department of Orthopaedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No.2 Yinghua East Street, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China. ; Haibo Zou:1.Department of Orthopaedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, No.2 Yinghua East Street, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China. ;
期刊:hASCs-derived exosomal miR-155-5p targeting TGFβR2 promotes autophagy and reduces pyroptosis to alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration
影响因子 :6.6
-
BSHXF-medicated serum combined with ADSCs regulates the TGF-β1/Smad pathway to repair oxidatively damaged NPCs and its component analysis (2023-06-03)
作者:Jiahao Duan:1.Hunan University of TCM, Changsha, Hunan, 410208, China; The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: 286118761@qq.com. ; Zhaoyong Li:1.The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: 191644929@qq.com. ; Enxu Liu:1.Hunan University of TCM, Changsha, Hunan, 410208, China; The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: lexdoctor@163.com. ; Hongping Long:1.The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: longhongping84@163.com. ; Long Chen:1.The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: 946196756@qq.com. ; Shaofeng Yang:1.The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, 410007, China. Electronic address: 574996585@qq.com. ;
期刊:BSHXF-medicated serum combined with ADSCs regulates the TGF-β1/Smad pathway to repair oxidatively damaged NPCs and its component analysis
影响因子 :5.4
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
microRNA-365 attenuated intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by targeting EFNA3 (2023-11-27)
作者:Chao Jiang:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Youjun Liu:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Weigong Zhao:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Yimin Yang:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Zhiwei Ren:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Xiaohui Wang:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; 2.Department of Developmental Genetics, Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Bad Nauheim, Germany. ; Dingjun Hao:1.Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China. ; Heng Du:1.Dep
期刊:microRNA-365 attenuated intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by targeting EFNA3
影响因子 :5.3
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液 (双抗),100×
-
Retinoic acid inhibits the pyroptosis of degenerated nucleus pulposus cells by activating Sirt1-SOD2 signaling (2023-04-02)
作者:Peng-Fei Li:1.Department of orthopedics, 2nd Affiliated Hospital (Jiande Branch), School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. ; Fei Xiong:1.Department of orthopedics, 2nd Affiliated Hospital (Jiande Branch), School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. ; Hong-Yuan Xing:1.Department of orthopedics, 2nd Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. ; 2.Orthopedics Department, Key Laboratory of musculoskeletal System Disease Research and Precision Therapy of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, PR China. ; Shao-Jun Hu:1.Department of orthopedics, 2nd Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China. ; 2.Orthopedics Department, Key Laboratory of musculoskeletal System Disease Research and Precision Therapy of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, PR China. ; Ning Zhang:1.Department of orthopedics, 2nd Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangz
期刊:Retinoic acid inhibits the pyroptosis of degenerated nucleus pulposus cells by activating Sirt1-SOD2 signaling
DOI:10.1080/03008207.2023.2192286
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Overloaded axial stress activates the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells of adult degenerative scoliosis combined with intervertebral disc degeneration (2023-04-08)
作者:Zhijun Cai:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, China. ; Qibiao Luo:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, China. ; Xi Yang:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, China. ; Luqiao Pu:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, China. ; Haiyang Zong:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, China. ; Rongmao Shi:1.Department of Orthopedics, The People's Liberation Army Joint Logistic Support Force 920th Hospital, No. 212 Daguan Rd, Kunming, Yunnan, 650032, Chi
期刊:Overloaded axial stress activates the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells of adult degenerative scoliosis combined with intervertebral disc degeneration
DOI:10.1007/s11033-023-08390-9
影响因子 :2.8
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Experimental study of miR-503 regulating the activity as well as the function of degenerated human nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc through inhibiting Wnt pathway. (2023-03-01)
作者:Xiaoming Shi:1.Orthopedics First ward, The First Hospital of Qiqihar, Affiliated Qiqihar Hospital of Southern Medical University, P.R. China. ; Shaohua Tian:1.Orthopedics Second ward, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical College, P.R. China. ; Yinan Tian:1.Neurology Second ward, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical College, P.R. China. ;
期刊:Experimental study of miR-503 regulating the activity as well as the function of degenerated human nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc through inhibiting Wnt pathway.
DOI:PMID:36856108
影响因子 :1.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes are beneficial to suppressing inflammation and promoting autophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration (2023-03-22)
作者:Baicheng Yang:1.Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou, Hebei, China. ; Xinming Yang:1.Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou, Hebei, China. yxm11200@126.com. ;
期刊:Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes are beneficial to suppressing inflammation and promoting autophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration
影响因子 :1.2
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Exogenous Klotho ameliorates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the Rac1/PAK1/MMP-2 signaling axis (2022-08-08)
作者:Yu-Yang Yi:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China. ; Hao Chen:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China. ; Shu-Bao Zhang:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China. ; Hao-Wei Xu:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China. ; Xin-Yue Fang:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China. ; Shan-Jin Wang:1.Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China; Department of orthopedic, East Hospital, Ji'an Hospital, Jinggangshan University School of Medicine, Jiangxi, China. Electronic address: kingspine@163.com. ;
期刊:Exogenous Klotho ameliorates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the Rac1/PAK1/MMP-2 signaling axis
影响因子 :5.5
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
The protective effects of dezocine on interleukin-1β-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and the possible mechanisms (2001-02-20)
作者:Fang Zhu:1.Department of Pain, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. ; Wei Duan:1.Dental Department, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. ; Chao Zhong:1.Department of Pain, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. ; Bing Ji:1.Department of Pain, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. ; Xinjun Liu:1.Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. ;
期刊:The protective effects of dezocine on interleukin-1β-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and the possible mechanisms
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2021.2017700
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Kukoamine A attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis, extracellular matrix degradation, and inflammation in nucleus pulposus cells by activating the P13K/Akt pathway (2003-02-20)
作者:Dan Wang:1.College of Acupuncture and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China. ; 2.Department of Spine Surgery, Jinmen NO. 2 People's Hospital, Jingmen, China. ; 3.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, PLA Middle Military Command General Hospital, Wuhan, China. ; Hao Qu:1.College of Acupuncture and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China. ; 2.Department of Orthopaedics, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Integrated Chinese & Western Medicine, Wuhan, China. ; Hui Kang:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, PLA Middle Military Command General Hospital, Wuhan, China. ; Feng Xu:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, PLA Middle Military Command General Hospital, Wuhan, China. ; Wei Huang:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Jinmen NO. 2 People's Hospital, Jingmen, China. ; Xianhua Cai:1.College of Acupuncture and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China. ; 2.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, PLA Middle Military Command General Hospit
期刊:Kukoamine A attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis, extracellular matrix degradation, and inflammation in nucleus pulposus cells by activating the P13K/Akt pathway
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2022.2051855
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
MicroRNA-137 inhibits the inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells by targeting activin a receptor type I (2003-02-20)
作者:Bin Yu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Ziqi Zhu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Beiduo Shen:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Jiawei Lu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Kai Guo:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Weidong Zhao:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ; Desheng Wu:1.Department of Spine Surgery, Shanghai East Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China. ;
期刊:MicroRNA-137 inhibits the inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells by targeting activin a receptor type I
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2022.2042987
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Lumican silencing alleviates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and senescence by inhibiting apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1/p38 signaling pathway via inactivating Fas ligand expression (2009-01-20)
作者:Zhenqiang Li:1.Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China. ; Chengfeng Sun:1.Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China. ; Maosong Chen:1.Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China. ; Boding Wang:1.Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China. ;
期刊:Lumican silencing alleviates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and senescence by inhibiting apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1/p38 signaling pathway via inactivating Fas ligand expression
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2021.1973781
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
miR‑489‑3p overexpression inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis, inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation via targeting Toll‑like receptor 4 (2009-01-20)
作者:Ling Dong:1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Guizhou Orthopedics Hospital, Guiyang, Guizhou 550000, P.R. China. ; Bo Dong:1.Pain Rehabilitation Department of TCM Orthopedic Center, Honghui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710054, P.R. China. ;
期刊:miR‑489‑3p overexpression inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis, inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation via targeting Toll‑like receptor 4
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
MiR-330-5p inhibits intervertebral disk degeneration via targeting CILP (2007-01-20)
作者:Shangzhi Li:1.Department of Orthopaedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, 300211, People's Republic of China. ; Jinwei Liu:1.Department of Orthopaedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, 300211, People's Republic of China. ; Liang Chen:1.Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Liaocheng People's Hospital, Liaocheng, 252000, Shandong, People's Republic of China. a13863503520@126.com. ;
期刊:MiR-330-5p inhibits intervertebral disk degeneration via targeting CILP
DOI:10.1186/s13018-021-02582-4
影响因子 :2.6
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
CircRNA RERE Promotes the Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through the miR-299-5p/Galectin-3 Axis (2012-01-20)
作者:Rong Wang:1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Anningshi First People's Hospital, 2 Henan Road, 650302 Anning, Yunnan, China. ; Xingchao Zhou:1.Equipment Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dali University, 32 Jiashibai Road, 671000 Dali, Yunnan, China. ; Guorui Luo:1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Anningshi First People's Hospital, 2 Henan Road, 650302 Anning, Yunnan, China. ; Jin Zhang:1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Anningshi First People's Hospital, 2 Henan Road, 650302 Anning, Yunnan, China. ; Min Yang:1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Anningshi First People's Hospital, 2 Henan Road, 650302 Anning, Yunnan, China. ; Chao Song:1.Pain Management, Anningshi First People's Hospital, 2 Henan Road, 650302 Anning, Yunnan, China. ;
期刊:CircRNA RERE Promotes the Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through the miR-299-5p/Galectin-3 Axis
影响因子 :0.0
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Micro Fragmented Adipose Tissue Promotes the Matrix Synthesis Function of Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Regenerates Degenerated Intervertebral Disc in a Pig Model: (2002-00-20)
作者:Xiaopeng Zhou:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. ; 2.Department of Orthopedics Research Institute of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. ; 3.These authors contributed equally to this article. ; Feng Zhang:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. ; 2.Department of Orthopedics Research Institute of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. ; 3.These authors contributed equally to this article. ; Dawei Wang:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. ; 2.These authors contributed equally to this article. ; Jingkai Wang:1.Department of Orthopedics Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospi
期刊:Micro Fragmented Adipose Tissue Promotes the Matrix Synthesis Function of Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Regenerates Degenerated Intervertebral Disc in a Pig Model:
影响因子 :3.3
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Role of lncRNA PART1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and associated underlying mechanism (2012-00-20)
作者:Zongyu Zhang:1.Department of Orthopedics, Lianyungang Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Lianyungang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Lianyungang, Jiangsu 222004, P.R. China. ; Yongfeng Huo:1.Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kangda College of Nanjing Medical University, Xuzhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang, Jiangsu 222004, P.R. China. ; Zhijing Zhou:1.Department of Orthopedics, Lianyungang Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Lianyungang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Lianyungang, Jiangsu 222004, P.R. China. ; Peng Zhang:1.Department of Orthopedics, Lianyungang Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Lianyungang Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Lianyungang, Jiangsu 222004, P.R. China. ; Jun Hu:1.Department of Orthopedics, Lianyungang Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Lianyungang Traditional Chin
期刊:Role of lncRNA PART1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and associated underlying mechanism
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
-
Dimethyl fumarate protects nucleus pulposus cells from inflammation and oxidative stress and delays the intervertebral disc degeneration (2010-00-20)
作者:Hainian Zhu:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Gang Chen:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Yuhua Wang:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Xuchen Lin:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Jingyuan Zhou:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Zengshun Wang:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ; Nanangxiu Suo:1.Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.R. China. ;
期刊:Dimethyl fumarate protects nucleus pulposus cells from inflammation and oxidative stress and delays the intervertebral disc degeneration
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: 人椎间盘髓核细胞
FAQs
Q:原代上皮细胞是否可以用除鼠尾胶原外的其他的包被试剂包被
A:理论上各种包被试剂都是具有增加吸附性的效果,鼠尾胶原蛋白I型是一种常用的细胞外基质成分,能够模拟体内细胞生长的真实环境,特别适合于促进上皮细胞等需要良好贴壁的细胞类型贴附和生长。上皮细胞在体内外都需要特定的细胞-细胞和细胞-基质相互作用才能正常增殖和分化,鼠尾胶原能够提供这样的有利基质,帮助细胞更好地粘附和伸展,从而维持正常的细胞功能和形态。
产品资料


识别码示意图